目录:
反转链表II
描述
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]
提示:
链表中节点数目为 n
1 <= n <= 500
-500 <= Node.val <= 500
1 <= left <= right <= n思路
- 左端节点不是起始节点
- 找到左端点的前一个节点 leftpointer_1 + 左端点 leftpointer
- 反转从左端点开始的 righ-left 个节点,并保留右端点 prev、右端点的下一个节点 rightpointer_1
- 左端节点 leftpointer 的next指向右端点的下一个节点 rightpointer_1
- 左端点的前一个节点 leftpointer_1 的next指向右端点
- 返回 head 头节点
- 左端节点是起始节点(head)
- 左端点的前一个节点 leftpointer_1 为 null
- 反转从左端点开始的 righ-left 个节点,并保留右端点 prev、右端点的下一个节点 rightpointer_1
- 左端节点 leftpointer 的next指向右端点的下一个节点 rightpointer_1
- 返回右端节点 prev
代码
struct ListNode* reverseBetween(struct ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
struct ListNode* leftpointer_1, * rightpointer_1;
leftpointer_1 = rightpointer_1 = head;
int leftmove = left - 2;
int rigthmove = right - left;
int temp = rigthmove;
if (temp == 0 || temp < 0) return head;
if (leftmove == -1) leftpointer_1 = NULL;
else
{
while (leftmove > 0 && leftpointer_1->next)
{
leftpointer_1 = leftpointer_1->next;
leftmove--;
}
}
struct ListNode* prev = leftpointer_1;
struct ListNode* curr, * leftpointer;
if (leftpointer_1) curr = leftpointer = leftpointer_1->next;
else curr = leftpointer = head;
while (curr && temp >= 0) {
struct ListNode* next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
temp--;
rightpointer_1 = curr;
}
if (leftpointer_1) {
leftpointer_1->next = prev;
leftpointer->next = rightpointer_1;
return head;
}
else {
leftpointer->next = rightpointer_1;
return prev;
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N) 其中 N 是链表总节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整个链表。
空间复杂度 O(1) 只使用到常数个变量
优秀思路
方法1:
与我们的方法非常类似,但在编码的过程中,采用了虚拟头节点的方式,避免了左端点是否是起始点的分类讨论。
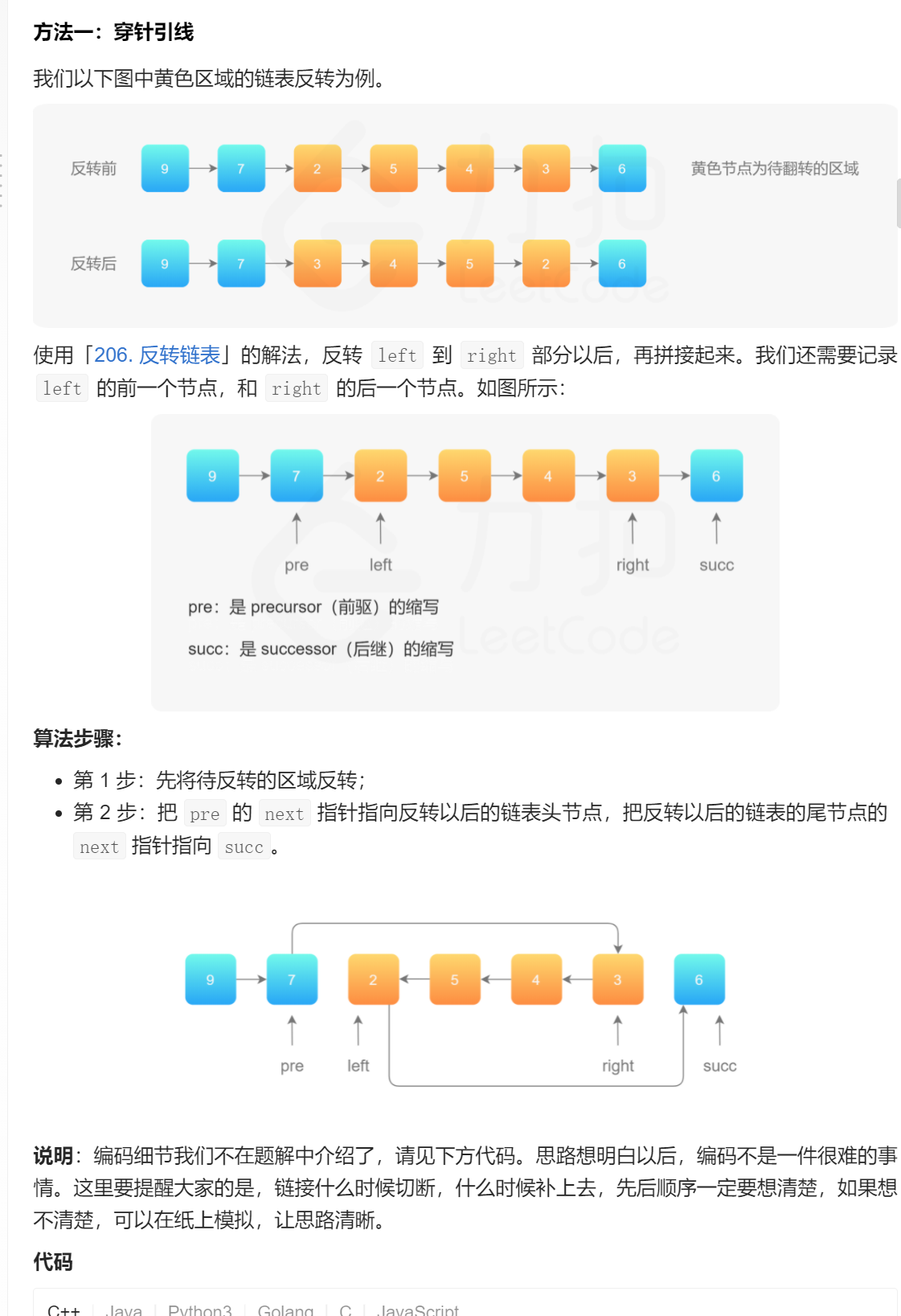
代码
struct ListNode *reverseBetween(struct ListNode *head, int left, int right) {
// 因为头节点有可能发生变化,使用虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论
struct ListNode *dummyNode = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummyNode->val = -1;
dummyNode->next = head;
struct ListNode *pre = dummyNode;
// 第 1 步:从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,来到 left 节点的前一个节点
// 建议写在 for 循环里,语义清晰
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre->next;
}
// 第 2 步:从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,来到 right 节点
struct ListNode *rightNode = pre;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
rightNode = rightNode->next;
}
// 第 3 步:切断出一个子链表(截取链表)
struct ListNode *leftNode = pre->next;
struct ListNode *curr = rightNode->next;
// 注意:切断链接
pre->next = NULL;
rightNode->next = NULL;
// 第 4 步:同第 206 题,反转链表的子区间
reverseLinkedList(leftNode);
// 第 5 步:接回到原来的链表中
pre->next = rightNode;
leftNode->next = curr;
return dummyNode->next;
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/solution/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-ii-by-leetcode-solut-teyq/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)时间复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N) 其中 N 是链表总节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整个链表。
空间复杂度 O(1) 只使用到常数个变量
方法二
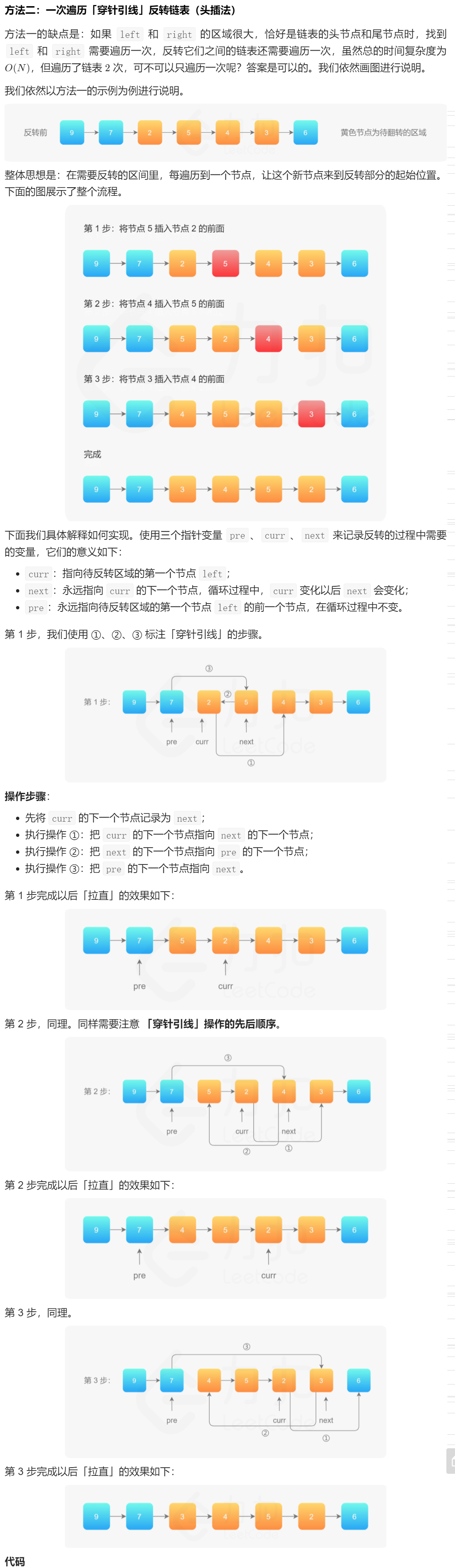
代码
struct ListNode *reverseBetween(struct ListNode *head, int left, int right) {
// 因为头节点有可能发生变化,使用虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论
struct ListNode *dummyNode = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummyNode->val = -1;
dummyNode->next = head;
struct ListNode *pre = dummyNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre->next;
}
struct ListNode *cur = pre->next;
struct ListNode *next;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = pre->next;
pre->next = next;
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/solution/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-ii-by-leetcode-solut-teyq/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。时间复杂度分析
时间复杂度 O(N) 其中 N 是链表总节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整个链表。
空间复杂度 O(1) 只使用到常数个变量

